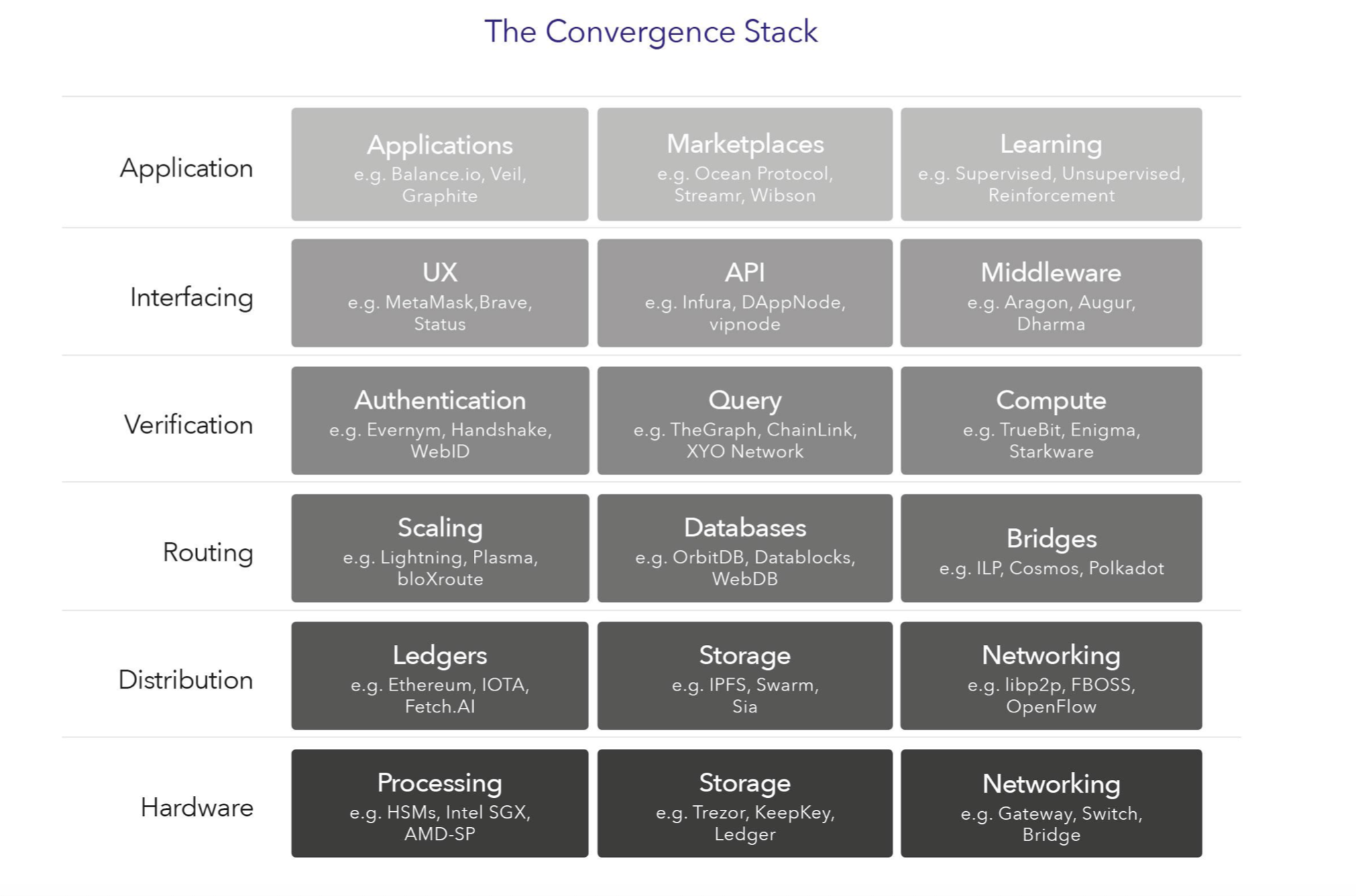
The Convergence Stack recognises how data is collected, transported and exchanges in marketplaces that function both economically and for technology innovation that consists of many moving parts. By bringing these elements together we will create value and investable urban business models.
Download the paper here to understand more.
Building the digital infrastructure for the Fourth Industrial Revolution
As our greatest challenges become increasingly global, and technological progress continues its exponential march, cities are once again coming to the fore. Nations are struggling to address global challenges like climate change, migration, and an integrated global economy supercharged by the Internet. Cities do not suffer from the same level of constitutional weight and are able to be more flexible and adaptable to the fast-changing technological, cultural and economic landscape. As the scale of emerging and present threats are presented globally, such as climate change and migration, the nation is no longer able to deliver effective policy responses.
Cities, on the other hand, offer a solution, as they reinforce collaboration and globalism to tackle these global problems regardless of national borders. It is the city that has the flexibility and opportunity to grasp the opportunities emerging from the coming Fourth Industrial Revolution and make a real and lasting impact. Cities must lead the revolution by utilizing data and emerging technologies in an open, collaborative, and shared way to build the digital infrastructure required to support a global, integrated and dynamic economy.
Renewal of the city
By 2050, 68% of the world’s population will live in cities. These megacities will be producing more than 80% of the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and will come to resemble the ancient state-cities of Athens, Rome, and Carthage – but this time round, they will be fueled by data. These poles of attraction tend to have similar challenges to nations around infrastructure, connectivity, mobility, and healthcare and have developed their own distinct cultural and economic micro-climates. Broken business models and misaligned incentives between different city stakeholders have restrained innovation and limited sustainable and inclusive growth.
Public-private partnerships are a start and have fostered collaboration between corporations and governments by aligning the business models while ensuring solutions meet the needs of citizens, not just shareholders. Cities, just like communication networks, benefit from network effects – the more citizens join, the more collaboration, innovation and economic output it produces. The challenge comes in connecting people, assets and data to take advantage of these city network effects.

The smart city: a testbed for new economic models
A global economic transformation characterized by the proliferation of service industries that may replace even heavy industries and manufacturing is also reflected in smart cities.
We are shifting from the current closed value chain towards an open value ecosystem. Energy production is undertaken by industrial and corporate energy vendors in a centralized manner, distributed to gas stations and then consumed in a rigid one-way transactional fashion. In the coming open value ecosystem, energy can be produced with solar panels, distributed on a transactive blockchain-based smart grid and consumed by the consumers (prosumers). Digitization turns our passive tools active. As infrastructure and energy trend towards commoditization, new economic value emerges from the production, collection, and analysis of data. This trend is reflected in all the other segments of smart cities.
Participants such as citizens, prosumers, software companies and local entrepreneurs who previously captured little to no value are now capturing more of that value. The success of this value-driven ecosystem depends on the premise that the right mechanisms are put in place to incentivize participants to share data and break current data silos. Let us explore the collection, safe storage, distribution and utilization of data through the Convergence Stack.
The Convergence Stack in smart cities
In the Convergence Stack, data is the core asset. Covering hardware, software, networking and applications, the stack underpins a private, secure, and decentralized digital infrastructure all coordinated by crypto-tokens. This new infrastructure requires a host of technologies from the hardware to secure the data to the tools to distribute the data like distributed ledgers. It will also need new routing and authentication technologies, interfacing technologies to make it easier to build applications, and new services, marketplaces and applications for users to benefit from what we hope to be a more equitable digital infrastructure.
The current centralized data infrastructure is broken. It is broken from a technical perspective. It is broken from a security and privacy perspective. And it is nowhere near ready to handle the convergence of technologies and markets in a smart city environment. We need a new digital infrastructure. As cities become the preeminent arena for economic growth and global problem-solving, we expect to see city-states lead to the development of digital infrastructure to support the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
For smart cities to thrive and be successful, they need to look beyond specific technologies or desires of particular industries. They must take a holistic and integrated view and see the emerging decentralized digital ecosystem as an opportunity to be grasped. They need to see that the internet of things, blockchain technology, and artificial intelligence are all interconnected. These technologies form the backbone of a trusted digital infrastructure.
Only once a new trusted digital infrastructure has been installed can the benefits of a truly smart city be shared widely and equitably. Outlier Ventures is embarking on a journey with Smart Dubai to apply the Convergence Stack on the city’s decentralised and open data infrastructure.
Download the paper here to understand more:

This article is for information purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. This article does not amount to an invitation or inducement to buy or sell an investment nor does it solicit any such offer or invitation in any jurisdiction.
In all cases, readers should conduct their own investigation and analysis of the data in the article. All statements of opinion and/or belief contained in this article and all views expressed and all projections, forecasts or statements relating to expectations regarding future events represent Outlier Ventures Operation Limited own assessment and interpretation of information available as at the date of this article.
No responsibility or liability is accepted by Outlier Ventures Operations Limited or Sapia Partners LLP for reliance on the contents of this article.
Outlier Ventures is an Appointed Representative of Sapia Partners LLP, a firm authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).